لغة إنجليزية 2
مخطط الموضوع
-

The level is first year, basic composition, social sciences, second semester
Education unit is horizontal. Subject. English foreign language. Lab 01
duration 1.5 H
-

Mr. Bokreta Farouk
Department of Social Sciences, Faculty of Social Sciences and Humanities, University of Djilali Bounaama, Khemis Miliana
gmail. faroukdidier57@gmail.com
available on sunday 08:30_15:00
-

This scale aims at a quantitative distribution of concepts related to the scale
Helps identify differences between overlapping concepts
Knowledge of gradation in sociological research
-

The student must be familiar with the basic rules of the language
To be familiar with the most basic terms in sociology
To understand the difference between academic language and non-academic language
-

trying to understand the concept of scale
We give an overview of the most important of the community lessons
The difference between the concept of sociology and other fields
-

In this chapter, we will seek to clarify the most important points that the researcher relies on in choosing his research
As well as identifying the factors affecting the researcher's direction
-

Sociology is a diverse and pluralistic discipline. There are a variety of socially located standpoints, each with its own truths and an equal right to be heard in sociological debates. For this reason, no single and coherent body of ideas acceptable to all practitioners can be set down. Many commentators have drawn the conclusion that sociological concepts are, therefore, ‘essentially contested’: that there can be no agreed and binding definition of any of the principal concepts used by sociologists in their research. This would seem to pose serious problems for anyone attempting to compile a dictionary or glossary of sociological concepts
-
-
Sociology emerged in the context of the sweeping changes that the Industrial Revolution brought to Europe. Two other factors operating at the time also encouraged the development of sociology. The example of natural sciences if there methods could make so much sense of the physical world could they not be applied successfully to the social world. The second factor was the exposure of Europe to the radically different societies that their colonial empires had taken over. Information about the contrasting social practices of these societies raised fresh questions about society in general. Auguste Comte (1798-1857) holds the title of Father of Sociology who established two specific problems for sociological investigation - social statics and social dynamics. Social statics refers to the problem of order and stability and social dynamics refers to the problem of social change. He believed that a science of sociology should be based on systematic observation and classification. Herbert Spencer (1820-1903) applied the theory of organic evolution to human society and developed theory of social evolution. Karl Marx (1818-1883) saw social conflict and inevitability of revolution as part of the society. Durkheim emphasized the basic needs of the society comparing it to a living organism. Max Weber stressed the regular patterns of action that can be discerned and result from particular beliefs. All these men were reacting to the crisis brought about in society by the flood of ideas upon which the revolutions were borne. Each searched for the dynamics that would explain the underlying causes of social change and in doing so they were also searching for the basis of social order.
-
-
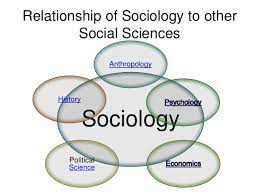
The key difference between sociology and social science is that the social sciences is a broad area which consists of many sub-fields and sociology is a subfield of social science. Sociology and social science are study
 fields that are dedicated to the study of human beings and society. In simpler terms
fields that are dedicated to the study of human beings and society. In simpler terms , it can be said that sociology is a sub-study branch of social science. Social science can be divided into various sub categories studying different aspects of society. Sociology, Political Science, History Studies, Law Studies are some examples for these sub-categories. Sociology, on the other hand, basically focuses on the human behavior and the features of a social structure. In this article, we are going to look at the differences between Sociology and Social Science in detail
, it can be said that sociology is a sub-study branch of social science. Social science can be divided into various sub categories studying different aspects of society. Sociology, Political Science, History Studies, Law Studies are some examples for these sub-categories. Sociology, on the other hand, basically focuses on the human behavior and the features of a social structure. In this article, we are going to look at the differences between Sociology and Social Science in detail -
-

American sociologist Gerhard Lenski defined society as is a
form of organization involving: (1) Relatively sustained ties of
interaction among its members. (2) Relatively high degree of
interdependence among its members. (3) A high degree of
autonomy -

-
Opened: الجمعة, 12 مايو 2023, 12:00 AMDue: الجمعة, 19 مايو 2023, 12:00 AM
-
-

1/ James Bonta , D. A. Andrews. The Psychology of Criminal Conduct , Sixth
Edition, New York , 20172/ Merlin Stone, when god was a women Houghton Mifflin Harcourt,
Publishing Company, 1978 -
