لغة إنجليزية
Aperçu des sections
-

Course Specifications for the Master 1 -Second Semester 2022/2023
Prof :D.MEZAINI Djilali
Subject
Level
A llocated Time per semester
coefficient
Credits
Evaluation
English
Master1
22.30
1
1
Continuous
This course is designed for « Master 1 » students . The principle aim of this course is to teach students to cope with input texts . However, students will also be expected to produce output texts in writing throughout the course.
This course focus mostly on key vocabulary for the discipline and on words and phrases commonly used in academic and scientific english. It also focuses on developing the skills that enable students to get most out written texts, journal articles, essays…etc . In addition to skills required to take part effectively in scientific forums,seminars…etc.
-

University: University of Djilali Bounaama. College: College of Social Sciences and Humanities. Department: Department of Psychology and Educational Sciences.Level :Master1
2nd Semester 2023
SUBJECT :ENGLISH
Prof :D.MEZAINI
Balance: ,coefficient: 01 Teaching period: 14-16 weeks Hourly volume: 3 hours every 15 days Duration of the conference: one hour and a half.Communication: Email: d.mezaini@univ-dbkm.dz University platform: http://elearning.univ-km.dz -

Courses Objectives :
By the end of this series, the first year Master student is supposed to have gained knowledge and understanding of the following research methods and techniques,have been familiar with their related terms, and their associated strengths and weaknesses.
Research methods
Related content
Types of experiments
• Lab, field, natural and quasi.
Experimental design
repeated measures, independent groups, matched pairs.Control: random allocation and counterbalancing.
Observations
• Structured and unstructured, naturalistic and controlled, participant and non participant, covert and overt.
Self-reports
• Questionnaires, Interviews (structured, semi structured and unstructured
Experiments
• Lab, field, quasi.
-

-

summary:
1. LESSON ONE : EXPERIMENTS
2. LESSON TWO : EXPERIMENTAL DESIGN
3. LESSON THREE :PILOT STUDIES
4. LESSON FOUR:OBSERVATIONAL TECHNIQUES
5. LESSON FIVE : SELF-REPORT TECHNIQUES
-
This course is designed for « Master 1 » students . The principle aim of this course is to teach students to cope with input texts . However, students will also be expected to produce output texts in writing throughout the course.
This course focus mostly on key vocabulary for the discipline and on words and phrases commonly used in academic and scientific english. It also focuses on developing the skills that enable students to get most out written texts, journal articles, essays…etc . In addition to skills required to take part effectively in scientific forums,seminars…etc.
Content Overview
Assessment Overview
· Planning, conducting, analysing and reporting psychological research across a range of experimental and non-experimental methodologies and techniques.
· Introduces some of the central areas of investigation in psychology organised in key themes.
The assessment section includes questions that allow students to demonstrate their ability to:
- Draw together their skills, knowledge and understanding from across the full course of study.
- Provide extended responses.
· Answer multiple choice questions. These contain four options each (one correct answer) and are worth one mark per question. These can assess any part of the course.
-

Specific aims :
- By the end of the lesson students will be able to identify the different types of experiments and their associated strengths and weaknesses.
-
-
-
Ouvert le : mardi 25 avril 2023, 00:00À remettre : mardi 2 mai 2023, 00:00
-
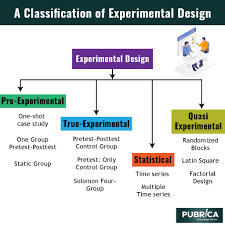
Specific aims :
- The key objectives are to familiarise students with:
- The different types of experimental designs: Independent measures and repeated measures.
- How participants are allocated to conditions of the independent variable in experiments using an Independent measures and repeated measures.
- The strengths and weaknesses of using these experimental designs.
- How these weaknesses can be overcome (for example using counterbalancing in repeated measures designs).
-
-
-
Ouvert le : mardi 25 avril 2023, 00:00À remettre : mardi 2 mai 2023, 00:00
-

Specific aims : By the end of the lesson the student will be familiar with :
- How to conduct pilot studies.
- The factors terms associated with pilot studies.
-
-
-
Ouvert le : mardi 25 avril 2023, 00:00À remettre : mardi 2 mai 2023, 00:00
-

Specific aims :
By the end of the lesson students will be able to :
- Grasp the meaning and types of observational techniques.
- Develop an understanding of issues surrounding collecting, analysing and interpreting observational data and understanding of how observational research can be refined by use of behavioural categories.
- Outline event and time samplin
- Explain how to implement event and time sampling.
- Design an observational activity using event sampling.
-
-
-
Ouvert le : mardi 25 avril 2023, 00:00À remettre : mardi 2 mai 2023, 00:00
-

Specific aims :
By the end of the lesson students will be able to :
- Identify the different types of the self report techniques.
- Understand the characteristics of the self report techniques.
- Identify strengths and weaknesses of each type.
-
-
-
Ouvert le : mardi 25 avril 2023, 00:00À remettre : mardi 2 mai 2023, 00:00
-
-


